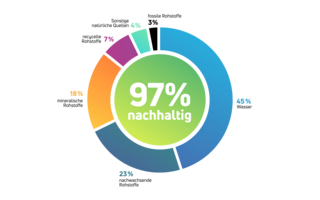
The individual raw material categories briefly explained:
The individual raw material categories briefly explained:
Proportion of fossil raw materials
Raw materials based on crude oil or natural gas. These are finite and pollute the environment during extraction and processing. At the end of their use, they are broken down into carbon dioxide and thus contribute to the greenhouse effect.
Proportion of mineral raw materials
These include chalk, titanium dioxide and quartz, for example. Although these natural materials are not renewable, they are found in large quantities in nature. Their production and use produce significantly fewer greenhouse gases than fossil raw materials. At the end of the product's life, they do not produce any climate-impacting carbon dioxide. Many of these raw materials will also be recycled in the future.
Proportion of renewable raw materials
Raw materials of plant origin such as vegetable oils, starch or cellulose. They grow back and can be obtained in an environmentally friendly way.
Proportion of recycled raw materials
Reused materials, e.g. from production waste or recycling processes. They save resources and reduce waste.
Proportion of Miscellaneous Natural Sources
This includes, for example, raw materials that are certified as sustainable using the mass balance method. This involves replacing fossil fuels with renewable raw materials - in a calculated and transparent manner in accordance with recognised standards.
Water content
Water serves as a solvent - it plays a central role in our environmentally friendly water-based paints in particular. Water is used in natural cycles and is therefore much more environmentally friendly than solvents.